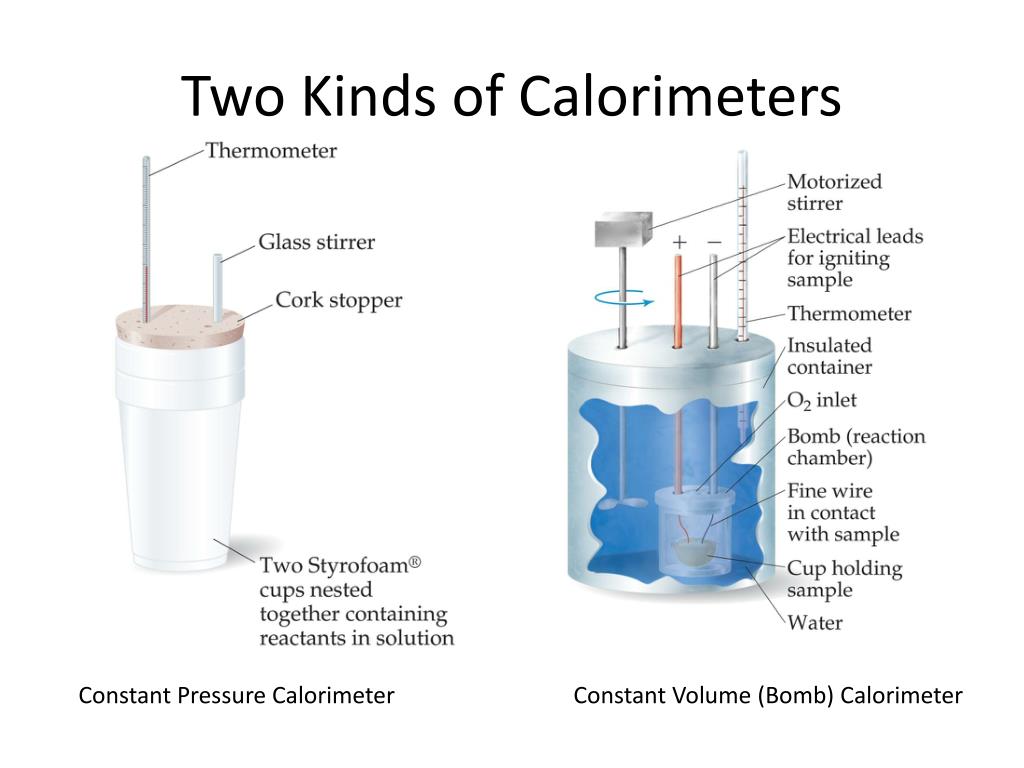
Calorimeter Constant Example Problems . A calorimeter is a device used to measure the amount of heat involved in a chemical or physical process. Example \(\pageindex{2}\) real calorimeter problem. For example, when an exothermic. When 40.0 ml of water at 60.0 °c is added to 40.0 ml at 25.0 °c water already in a calorimeter, the temperature rises 15.0 °c. What is t f when 2.00g au at 100.0°c is placed into 25.0 ml h 2 o at 30.0°c? When 1.0 g of fructose, c 6 h 12 o 6 (s), a sugar commonly found in fruits, is burned in oxygen in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the. When 1.0 g of fructose, c 6 h 12 o 6 (s), a sugar commonly found in fruits, is burned in oxygen in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the. In this set of practice questions, we will go over the main types of questions on calorimetry including the heat.
from www.slideserve.com
In this set of practice questions, we will go over the main types of questions on calorimetry including the heat. What is t f when 2.00g au at 100.0°c is placed into 25.0 ml h 2 o at 30.0°c? When 1.0 g of fructose, c 6 h 12 o 6 (s), a sugar commonly found in fruits, is burned in oxygen in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the. When 1.0 g of fructose, c 6 h 12 o 6 (s), a sugar commonly found in fruits, is burned in oxygen in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the. A calorimeter is a device used to measure the amount of heat involved in a chemical or physical process. Example \(\pageindex{2}\) real calorimeter problem. When 40.0 ml of water at 60.0 °c is added to 40.0 ml at 25.0 °c water already in a calorimeter, the temperature rises 15.0 °c. For example, when an exothermic.
PPT Calorimetry PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3850751
Calorimeter Constant Example Problems A calorimeter is a device used to measure the amount of heat involved in a chemical or physical process. A calorimeter is a device used to measure the amount of heat involved in a chemical or physical process. For example, when an exothermic. When 40.0 ml of water at 60.0 °c is added to 40.0 ml at 25.0 °c water already in a calorimeter, the temperature rises 15.0 °c. When 1.0 g of fructose, c 6 h 12 o 6 (s), a sugar commonly found in fruits, is burned in oxygen in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the. When 1.0 g of fructose, c 6 h 12 o 6 (s), a sugar commonly found in fruits, is burned in oxygen in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the. Example \(\pageindex{2}\) real calorimeter problem. What is t f when 2.00g au at 100.0°c is placed into 25.0 ml h 2 o at 30.0°c? In this set of practice questions, we will go over the main types of questions on calorimetry including the heat.
From materialschreiner.z19.web.core.windows.net
Calorimetry Sample Problems With Solutions Calorimeter Constant Example Problems What is t f when 2.00g au at 100.0°c is placed into 25.0 ml h 2 o at 30.0°c? For example, when an exothermic. Example \(\pageindex{2}\) real calorimeter problem. When 1.0 g of fructose, c 6 h 12 o 6 (s), a sugar commonly found in fruits, is burned in oxygen in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the. When. Calorimeter Constant Example Problems.
From www.youtube.com
CHEMISTRY 101 Calculating Change in Internal Energy Using Constant Calorimeter Constant Example Problems When 1.0 g of fructose, c 6 h 12 o 6 (s), a sugar commonly found in fruits, is burned in oxygen in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the. In this set of practice questions, we will go over the main types of questions on calorimetry including the heat. For example, when an exothermic. A calorimeter is a device. Calorimeter Constant Example Problems.
From www.chegg.com
Solved A bomb calorimeter, or constant volume calorimeter, Calorimeter Constant Example Problems When 1.0 g of fructose, c 6 h 12 o 6 (s), a sugar commonly found in fruits, is burned in oxygen in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the. When 40.0 ml of water at 60.0 °c is added to 40.0 ml at 25.0 °c water already in a calorimeter, the temperature rises 15.0 °c. What is t f. Calorimeter Constant Example Problems.
From www.youtube.com
Calorimetry at Constant Pressure YouTube Calorimeter Constant Example Problems Example \(\pageindex{2}\) real calorimeter problem. When 1.0 g of fructose, c 6 h 12 o 6 (s), a sugar commonly found in fruits, is burned in oxygen in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the. When 40.0 ml of water at 60.0 °c is added to 40.0 ml at 25.0 °c water already in a calorimeter, the temperature rises 15.0. Calorimeter Constant Example Problems.
From www.chegg.com
Solved A bomb calorimeter, or constant volume calorimeter, Calorimeter Constant Example Problems Example \(\pageindex{2}\) real calorimeter problem. When 1.0 g of fructose, c 6 h 12 o 6 (s), a sugar commonly found in fruits, is burned in oxygen in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the. When 1.0 g of fructose, c 6 h 12 o 6 (s), a sugar commonly found in fruits, is burned in oxygen in a bomb. Calorimeter Constant Example Problems.
From www.nagwa.com
Question Video Determining the Correct Formula to Use in Order to Calorimeter Constant Example Problems What is t f when 2.00g au at 100.0°c is placed into 25.0 ml h 2 o at 30.0°c? Example \(\pageindex{2}\) real calorimeter problem. When 1.0 g of fructose, c 6 h 12 o 6 (s), a sugar commonly found in fruits, is burned in oxygen in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the. When 1.0 g of fructose, c. Calorimeter Constant Example Problems.
From www.chegg.com
Solved In Problems I, II, And III Calorimeter Constant I... Calorimeter Constant Example Problems When 40.0 ml of water at 60.0 °c is added to 40.0 ml at 25.0 °c water already in a calorimeter, the temperature rises 15.0 °c. For example, when an exothermic. In this set of practice questions, we will go over the main types of questions on calorimetry including the heat. Example \(\pageindex{2}\) real calorimeter problem. A calorimeter is a. Calorimeter Constant Example Problems.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Thermochemistry PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5405762 Calorimeter Constant Example Problems When 1.0 g of fructose, c 6 h 12 o 6 (s), a sugar commonly found in fruits, is burned in oxygen in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the. When 1.0 g of fructose, c 6 h 12 o 6 (s), a sugar commonly found in fruits, is burned in oxygen in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the.. Calorimeter Constant Example Problems.
From www.bartleby.com
Answered In constantpressure calorimetry… bartleby Calorimeter Constant Example Problems What is t f when 2.00g au at 100.0°c is placed into 25.0 ml h 2 o at 30.0°c? For example, when an exothermic. Example \(\pageindex{2}\) real calorimeter problem. When 1.0 g of fructose, c 6 h 12 o 6 (s), a sugar commonly found in fruits, is burned in oxygen in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the. When. Calorimeter Constant Example Problems.
From www.youtube.com
Calorimetry, Bomb Calorimetry, Constant Pressure Calorimetry FULL Calorimeter Constant Example Problems What is t f when 2.00g au at 100.0°c is placed into 25.0 ml h 2 o at 30.0°c? In this set of practice questions, we will go over the main types of questions on calorimetry including the heat. A calorimeter is a device used to measure the amount of heat involved in a chemical or physical process. When 1.0. Calorimeter Constant Example Problems.
From www.tessshebaylo.com
Equation For Calorimetry Tessshebaylo Calorimeter Constant Example Problems A calorimeter is a device used to measure the amount of heat involved in a chemical or physical process. Example \(\pageindex{2}\) real calorimeter problem. What is t f when 2.00g au at 100.0°c is placed into 25.0 ml h 2 o at 30.0°c? In this set of practice questions, we will go over the main types of questions on calorimetry. Calorimeter Constant Example Problems.
From www.chegg.com
Calculate the calorimeter constant (From Lab) So for Calorimeter Constant Example Problems In this set of practice questions, we will go over the main types of questions on calorimetry including the heat. When 40.0 ml of water at 60.0 °c is added to 40.0 ml at 25.0 °c water already in a calorimeter, the temperature rises 15.0 °c. When 1.0 g of fructose, c 6 h 12 o 6 (s), a sugar. Calorimeter Constant Example Problems.
From www.chegg.com
Solved Use the Calorimeter Constant and equations provided Calorimeter Constant Example Problems What is t f when 2.00g au at 100.0°c is placed into 25.0 ml h 2 o at 30.0°c? When 40.0 ml of water at 60.0 °c is added to 40.0 ml at 25.0 °c water already in a calorimeter, the temperature rises 15.0 °c. When 1.0 g of fructose, c 6 h 12 o 6 (s), a sugar commonly. Calorimeter Constant Example Problems.
From www.youtube.com
Calorimetry calculation (constant pressure) Example 1 YouTube Calorimeter Constant Example Problems When 40.0 ml of water at 60.0 °c is added to 40.0 ml at 25.0 °c water already in a calorimeter, the temperature rises 15.0 °c. When 1.0 g of fructose, c 6 h 12 o 6 (s), a sugar commonly found in fruits, is burned in oxygen in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the. In this set of. Calorimeter Constant Example Problems.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Thermochemistry PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3207088 Calorimeter Constant Example Problems When 1.0 g of fructose, c 6 h 12 o 6 (s), a sugar commonly found in fruits, is burned in oxygen in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the. A calorimeter is a device used to measure the amount of heat involved in a chemical or physical process. When 40.0 ml of water at 60.0 °c is added to. Calorimeter Constant Example Problems.
From www.chegg.com
Solved How to calculate the calorimeter constant Calorimeter Constant Example Problems When 1.0 g of fructose, c 6 h 12 o 6 (s), a sugar commonly found in fruits, is burned in oxygen in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the. When 40.0 ml of water at 60.0 °c is added to 40.0 ml at 25.0 °c water already in a calorimeter, the temperature rises 15.0 °c. What is t f. Calorimeter Constant Example Problems.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Calorimetry PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1875569 Calorimeter Constant Example Problems When 1.0 g of fructose, c 6 h 12 o 6 (s), a sugar commonly found in fruits, is burned in oxygen in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the. What is t f when 2.00g au at 100.0°c is placed into 25.0 ml h 2 o at 30.0°c? When 40.0 ml of water at 60.0 °c is added to. Calorimeter Constant Example Problems.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Zumdahl Chapter 6 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4269919 Calorimeter Constant Example Problems When 1.0 g of fructose, c 6 h 12 o 6 (s), a sugar commonly found in fruits, is burned in oxygen in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the. When 40.0 ml of water at 60.0 °c is added to 40.0 ml at 25.0 °c water already in a calorimeter, the temperature rises 15.0 °c. In this set of. Calorimeter Constant Example Problems.